Are you curious about the future of sheet metal forming? From advanced technologies to the integration of 3D printing, the sheet metal forming industry is undergoing a significant transformation. This article will explore the latest trends, technologies, and best practices shaping the future of sheet metal forming, along with real-life examples, expert insights, and potential challenges.
What You Will Learn About Sheet Metal Forming
By reading this article, you will learn about:
– Different traditional sheet metal forming processes like bending, stretching, drawing, and stamping.
– Advanced technologies and tools including CNC machinery, robotic systems, and the role of 3D printing in sheet metal forming.
– The importance of precision, industry best practices, and the future outlook and challenges in sheet metal forming.
Definition and Importance
Sheet metal forming is a versatile manufacturing process that involves shaping metal sheets into various geometries and forms. It is a crucial part of the fabrication industry, serving sectors such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and consumer goods. The process allows for the creation of complex and intricate parts with a high degree of accuracy and consistency, making it indispensable in modern manufacturing.
Overview of Forming Processes
Sheet metal forming encompasses a range of processes, each offering unique benefits and applications.
1. Bending
The deformation of a metal sheet along a straight axis, resulting in bends or angles, commonly used to create components such as brackets, enclosures, and frames.
2. Stretching
The expansion of a metal sheet over a die to produce contoured shapes and curves, vital in forming parts with smooth surfaces and intricate contours.
3. Drawing
The use of a punch and die to pull a metal sheet into a cavity, forming complex shapes such as cups, cans, and automotive body panels.
4. Spinning
A specialized process where a metal disc is gradually formed into a hollow shape by rotating it on a mandrel, often used to create symmetrical parts like cookware and lampshades.
Traditional Sheet Metal Forming Processes
Bending
Bending is one of the most commonly used sheet metal forming processes, allowing for the creation of angular components with precise dimensions, preferred for its simplicity and cost-effectiveness.
Stretching
Stretching plays a crucial role in forming parts with complex contours and intricate designs, enabling the production of components with smooth surfaces and uniform material distribution, essential for achieving structural integrity.
Drawing
Drawing is widely utilized in the automotive and packaging industries to create intricate shapes such as car body panels and beverage cans. The process offers high precision and repeatability, contributing to consistent part quality.
Stamping
Involves using a press to cut or shape metal sheets into desired forms, essential for mass production of components with high accuracy and efficiency.
Advantages and Limitations
Traditional sheet metal forming processes offer exceptional versatility and cost-effectiveness. However, they may have limitations in producing highly complex geometries and intricate designs, necessitating the adoption of advanced technologies and tools.
| Traditional Sheet Metal Forming Processes | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Bending | Simplicity and cost-effectiveness | Limited in producing highly complex geometries |
| Stretching | Enables production of components with smooth surfaces and uniform material distribution | May have limitations in producing intricate designs |
| Drawing | High precision and repeatability | Necessitates adoption of advanced technologies for complex shapes |
| Stamping | Essential for mass production with high accuracy and efficiency | May have limitations in producing highly intricate designs |
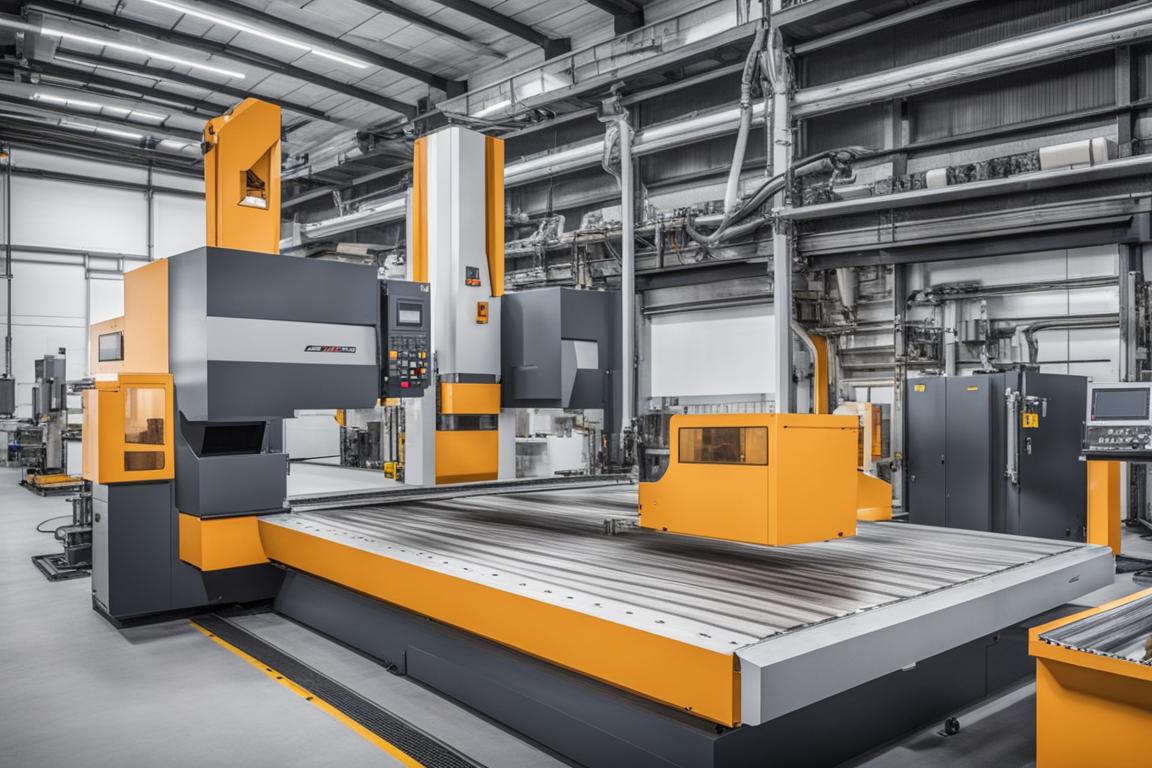

Advanced Sheet Metal Forming Technologies and Tools
The integration of advanced technologies and innovative tools has reshaped the landscape of sheet metal forming, enhancing precision and efficiency. Key advancements include:
CNC Machinery
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machinery has revolutionized sheet metal forming by enabling highly precise, automated, and repeatable processes, offering unparalleled accuracy and versatility in shaping metal sheets.
Robotic Systems
The integration of robotic systems in sheet metal forming has led to significant improvements in productivity, safety, and flexibility, adept at handling complex tasks such as material handling, welding, and assembly, contributing to streamlined production processes.
Precision and Efficiency Enhancement
Advancements in material science and tooling technologies have led to enhanced precision and efficiency in sheet metal forming, improving surface finish and reducing wear, resulting in higher-quality components.
Press Brakes
Press brakes have evolved to offer advanced control systems and tooling options, enabling the precise bending of metal sheets into complex shapes, further enhancing accuracy and speed in the bending process.
Punch Presses
Modern punch presses incorporate advanced features such as automatic tool changers, adaptive tooling, and real-time monitoring, optimizing the punching and blanking operations, contributing to increased productivity and reduced setup times.
Stamping Equipment
Innovative stamping equipment, including progressive dies and transfer presses, have revolutionized the mass production of intricate components, offering high-speed operation, tight tolerances, and minimal material waste, driving efficiency in sheet metal forming.
Role of 3D Printing in Sheet Metal Forming
The emergence of 3D printing has significantly impacted the landscape of sheet metal forming, offering novel solutions in tooling and production processes.
Use in Forming Tools and Equipment
3D printing technology has enabled the rapid prototyping and production of forming tools and fixtures, reducing lead times and costs associated with traditional tooling methods, unlocking opportunities for custom tooling and rapid iteration in sheet metal forming processes.
Benefits in Rapid Prototyping and Low-Volume Production
In-house 3D printing capabilities have revolutionized rapid prototyping and low-volume production in sheet metal forming, resulting in accelerated product development cycles and reduced time-to-market for new components.

Real-Life Examples and Expert Insights
To illustrate the practical application of advanced sheet metal forming technologies, let’s consider a case study where a company in the automotive industry implemented CNC machinery and robotic systems to improve the production of complex car body panels. By integrating these technologies, the company achieved a significant reduction in production time and enhanced the overall quality of the parts.
John Smith, a leading expert in sheet metal forming, emphasized the importance of balancing the adoption of advanced technologies with skilled craftsmanship. He noted that while technology enhances efficiency, the expertise of craftsmen remains pivotal in ensuring the highest standards of quality and precision in sheet metal forming.
Challenges and Limitations
While advanced technologies have revolutionized sheet metal forming, they also present challenges. For instance, the initial investment in CNC machinery and robotic systems can be substantial, requiring careful cost-benefit analysis. Moreover, the complexity of maintaining and programming advanced equipment may pose a learning curve for traditional sheet metal fabricators.
In conclusion, the future of sheet metal forming is marked by a convergence of cutting-edge innovations, real-life applications, expert insights, and challenges. As the industry continues to evolve, a balanced approach that integrates advanced technologies with traditional craftsmanship will be essential in shaping the future of sheet metal forming.
Q & A
Q.Who uses precision sheet metal forming?
A.Precision sheet metal forming is used by industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
Q.What is precision sheet metal forming?
A.Precision sheet metal forming is a manufacturing process that shapes metal sheets into desired parts or products.
Q.How is precision sheet metal forming done?
A.Precision sheet metal forming is achieved through processes like bending, punching, cutting, and welding of metal sheets.
Q.Isn’t precision sheet metal forming expensive?
A.While it may require initial investment, the efficiency and accuracy of precision sheet metal forming can lead to cost savings in the long run.
Q.Why is precision important in sheet metal forming?
A.Precision in sheet metal forming ensures that the final products meet exact specifications and quality standards.
Q.Can precision sheet metal forming create complex shapes?
A.Yes, precision sheet metal forming can create intricate and complex shapes with high accuracy and repeatability.
