Sheet metal forming is a core element in the crafting of products from cars to appliances – involving skill, experience and technologically advanced tools. This article provides an insight into how this intricate process works, discussing techniques used with metals to create superior quality components. From materials selection through shaping processes. Sheet metal forming can be seen as precise artistry that yields results of strength and endurance for all kinds of applications.
Key Takeaways
- Essential sheet metal forming techniques such as bending, curling and ironing are used to transform flat sheets into intricately shaped components.
- Advanced tools and technologies in sheet metal forming provide increased productivity, cost efficiency, flexibility & safety.
- Best practices for material selection & tool/equipment selection enable fabricators to reduce waste while upholding quality standards.
Essential Sheet Metal Forming Techniques
The process of sheet metal forming involves taking flat sheets of metal and transforming them into various parts with intricate shapes to serve multiple industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction among others. Utilizing a few techniques including bending, curling or ironing is essential when executing the desired shape during this method of metal forming. Cold forming press and stretch form are some methods that have been heavily employed in achieving different results from components which had started out simply as sheets at the onset of the said processes. Overall mastery over these techniques can generate functional yet decorative shaped products using metals for all intended purposes, be it architectural or industrial applications alike.
Bending
The metal bending process is used across a variety of industries, such as automotive, construction and aerospace. In the manufacturing industry, press brakes or punch presses are typically used to create precise control over the angle and radius of bend needed for complex shapes in sheets with material thicknesses that determine their rolling direction. Producing high quality sheet metal parts from pieces of metal while minimizing waste. It also allows transforming said materials into functional components with an aesthetically pleasing look. Bending facilitates increased strength, stiffness or improved aesthetics depending on how it’s applied during forming.
Curling
Sheet metal forming involves a process known as curling, in which sheet metal components are given smooth edges and cylindrical shapes by eliminating sharp edges or burrs. Curving provides extra safety due to its ability of getting rid of rugged areas that could be potentially dangerous during handling or use. There is a wide range of tools specifically designed for this purpose including hammers, wooden boards, horns, gauge irons and more. Carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum and copper have been recognized as the best materials suitable for such type of processing since they can increase not only durability but also improve product’s aesthetics until it meets high-quality standards before leaving the production line.
Ironing
Using a punch and die, sheet metal workpieces can be shaped by forcing the material through to achieve the desired form. This process is called ironing and it provides uniform wall thickness when used for aluminum cans production or deep drawing. It also helps minimize waste in materials as well as weak points caused by thin areas while achieving near-net shape forming of soft metals such as aluminum sheets with an excellent surface finish. Ironing has many advantages which are utilized in multiple industrial applications from construction and aerospace to automotive manufacturing industries requiring accurate components creation results.
Hydroforming
Hydroforming is a unique sheet metal forming technique that uses pressurized fluid to shape metal. This process is particularly useful when manufacturing complex shapes and structures, as it allows for greater flexibility in design and can create smoother, more consistent forms than traditional mechanical forming methods.
In hydroforming, a piece of sheet metal is placed into a die, and a high-pressure hydraulic fluid is then used to press the metal into the shape of the die. This process can be used to create a wide range of shapes and is often used in the automotive and aerospace industries to create parts with complex geometries.
One of the main advantages of hydroforming is that it can create parts with a higher strength-to-weight ratio than other forming methods. This is because the pressure from the hydraulic fluid is applied evenly across the entire piece of metal, reducing the risk of weak points or defects in the finished product.
Additionally, hydroforming can often be a more cost-effective method of production, as it requires fewer tools and less material than other methods. However, it’s worth noting that the initial setup costs can be higher due to the need for specialized equipment and dies.
Despite these potential drawbacks, hydroforming is a versatile and valuable technique in sheet metal forming, offering a unique combination of precision, efficiency, and flexibility.
Punching
Punching is another fundamental technique in sheet metal forming. This process involves creating holes in the metal sheet by applying a high force on it using a punch and a die. The punch is the tool that penetrates the metal to create the hole, while the die is located on the opposite side of the sheet, supporting the material and giving the hole its shape and size.
This method is highly efficient for mass production as it allows for the creation of multiple identical holes in a short amount of time. It is particularly useful in industries such as automotive and aerospace, where precision and consistency are key.
Punching, however, also has its limitations. The process can cause deformation around the edges of the hole, known as the “roll-over”, and can also lead to cracks in the metal if not done properly. The quality of the punch and die, along with the proper alignment and control of the punching force, are critical factors in ensuring a successful punching process.
Despite these challenges, punching remains a widely used and valuable technique in sheet metal forming, offering a combination of speed, accuracy, and efficiency.
Equipment Used in Sheet Metal Forming
| Equipment | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Press Brakes | Press brakes are used to bend sheet metal into the desired shape. They provide precise control over the angle and radius of the bend. | Typically used in the manufacturing industry to create complex shapes in sheets. |
| CNC Machines | CNC machines are automated tools that can precisely control cutting and shaping processes. | Ideal for sheet metal fabrication, as they can rapidly produce complex components with high precision. |
| Hydraulic Presses | Hydraulic presses use pressurized fluid to shape metal, allowing for greater flexibility in design and smoother, more consistent forms. | Particularly useful when manufacturing complex shapes and structures. |
| Rollers | Rollers are used to bend sheet metal into cylindrical shapes or to flatten it. | Used in various industries, including automotive and aerospace, for creating curved surfaces and removing wrinkles from sheet metal. |
| Punch Presses | Punch presses are used to create holes or indentations in the metal sheet. They provide high force and precision. | Used in industries such as automotive and aerospace, where precision and consistency are key. |
| Shears | Shears are used to make straight-line cuts on flat metal stock. They work by placing the flat metal stock between the blades and applying force. | Used in many metal fabrication workshops for cutting and trimming metal sheets. |
| Bending Machines | Bending machines are used to bend metal using force, pressure, heat, or through other means. | Used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and construction, for bending metal sheets into desired shapes. |
| Turret Punches | Turret punches are used to create various shapes in metal. They work by holding the metal sheet in place while the machine’s punches are used to create the desired shapes. | Used in industries such as manufacturing and construction, where there is a need for high speed and precision in creating various shapes in metal sheets. |
Material Selection for Sheet Metal Forming

In sheet metal forming, the selection of a suitable material is crucial for success. The choice depends on certain criteria such as formability, corrosion resistance, weldability and strength to weight ratio. Cost also being taken into account. Commonly used metals in sheet metal forming are aluminum, steel and stainless steel, each offering its own benefits.
Aluminum stands out due to its high malleable characteristics which make it more prone to distortion along with good welding ability making it perfect for various purposes while creating these sheets. This soft material resists rusting and offers great strength alongside lightness when compared with other materials used commonly in shape engineering activities like steels. Steel usually provides greater durability than aluminium thereby increasing defence from dentures or piercing damages but at higher costs sometimes involved too! Stainless steel, on the other hand, combines the best of both worlds. It has the durability and strength of steel along with the corrosion resistance of aluminum. This makes it a popular choice for projects that require both strength and aesthetics. Understanding the features associated with all mentioned aforementioned substances helps us identify the most ideal option depending upon project specifications laid down before any potential fabrication begins properly fulfilling a given purpose!
Advanced Tools and Technologies in Sheet Metal Forming
By utilizing up-to-date advances in tools and technology such as CNC machines and 3D printed forming equipment, sheet metal fabricators can optimize their abilities to create components with intricate designs and complex shapes through free formation techniques. This improvement in efficiency, accuracy, and adaptability allows for reduced production time while preserving quality outputs. These new technologies help lessen the waste created during manufacturing processes connected to metal forming of sheets.
Gallery: Custom 3D Printed Forming Tool by Atlas Manufacturing
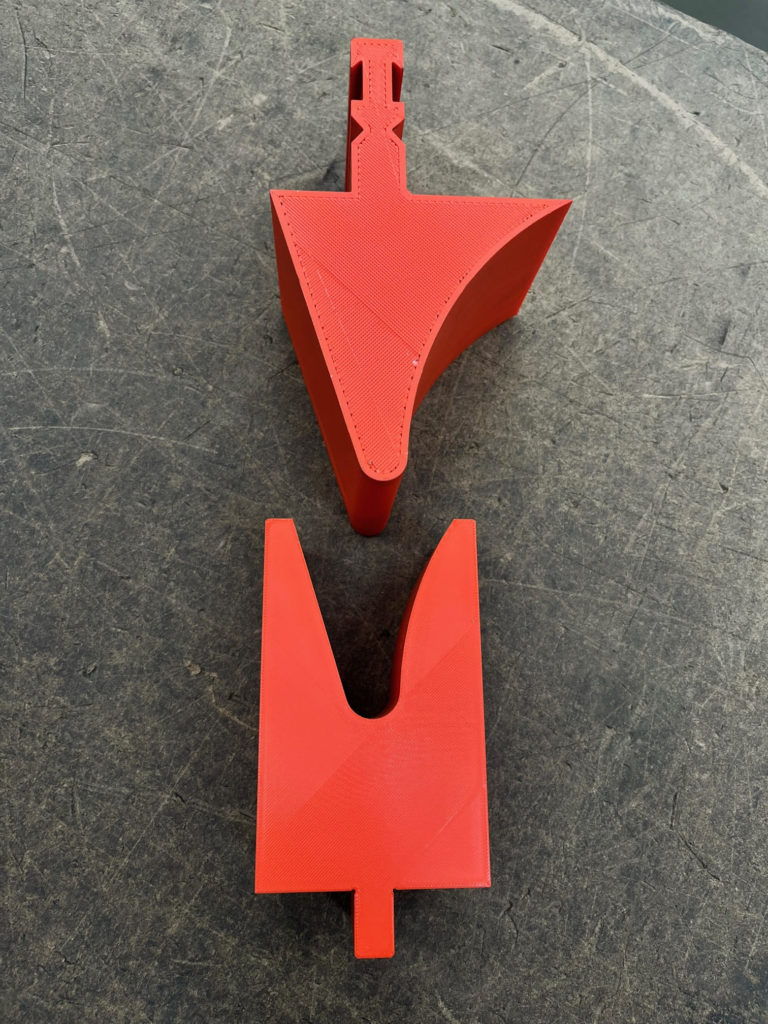
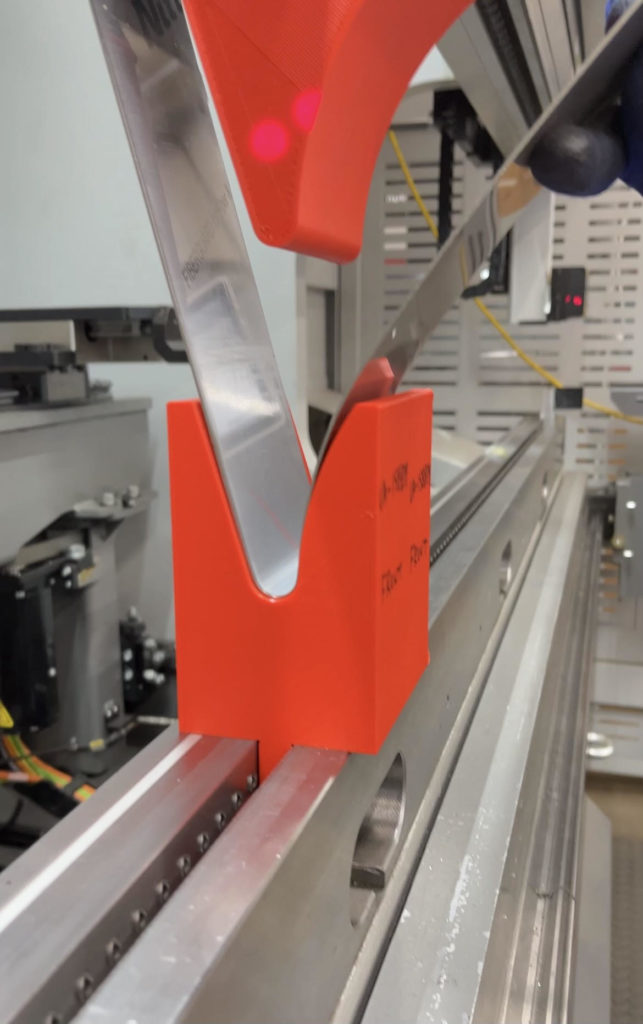
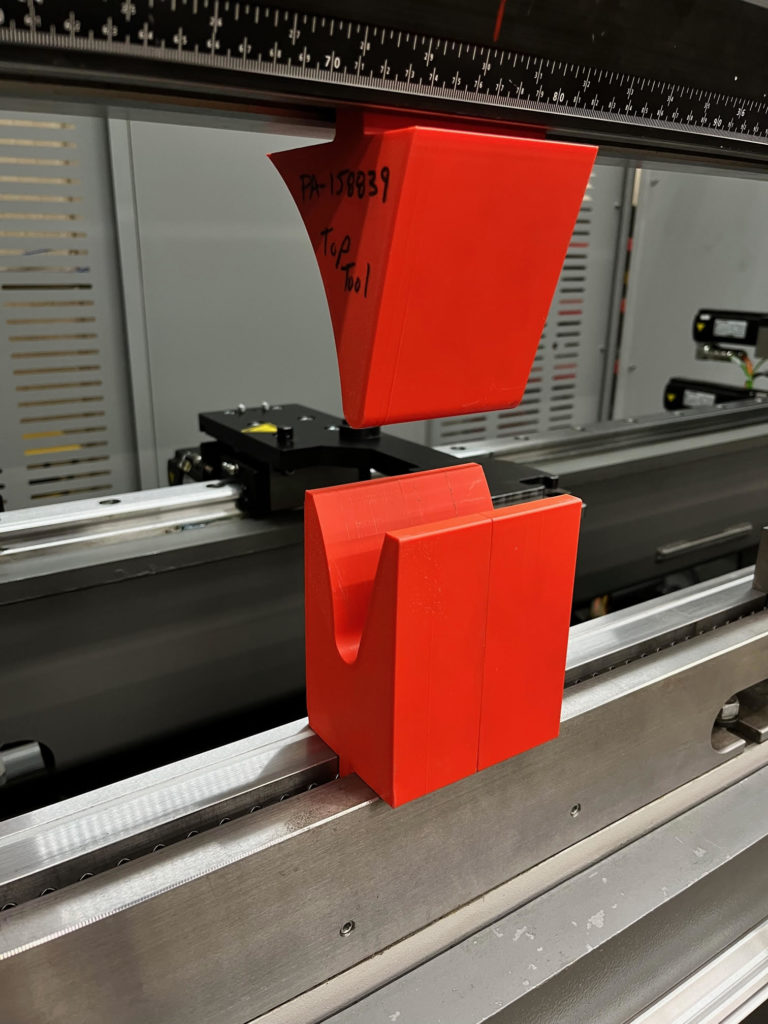
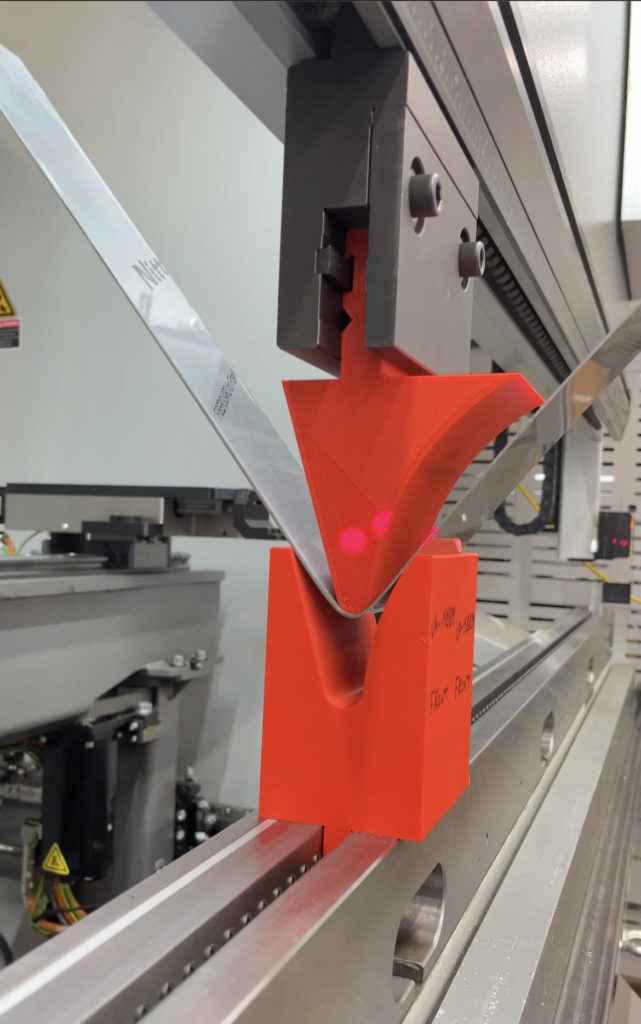
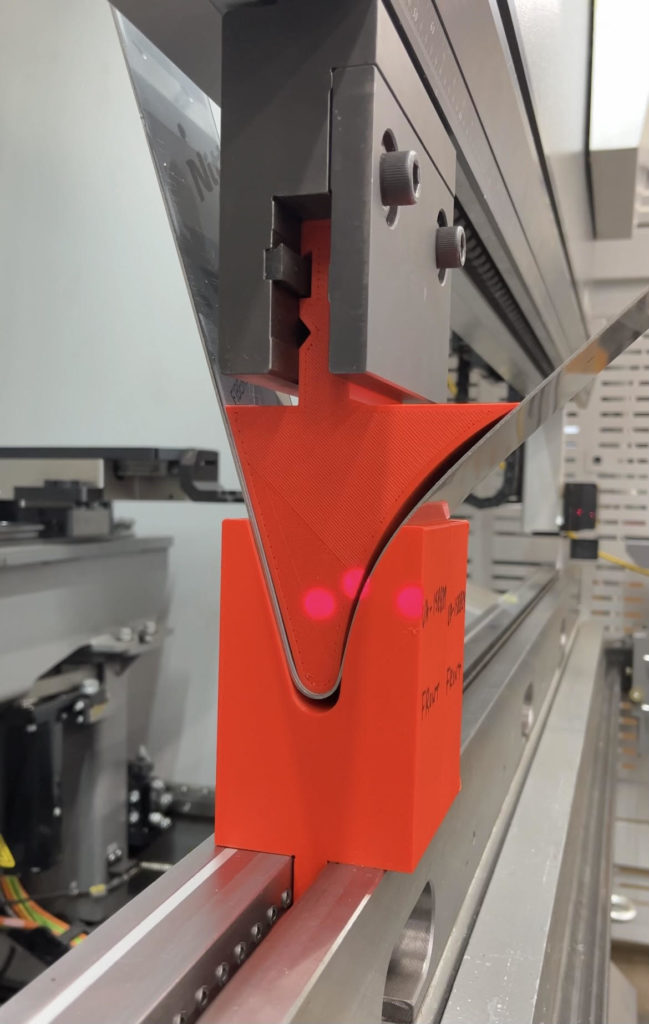
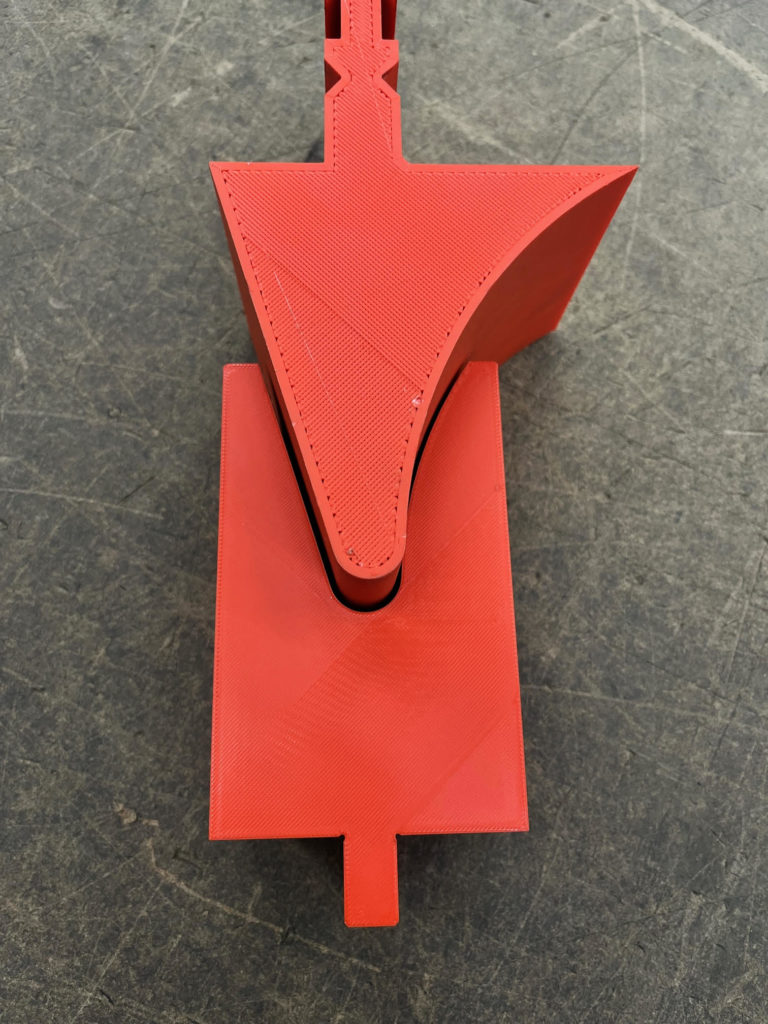


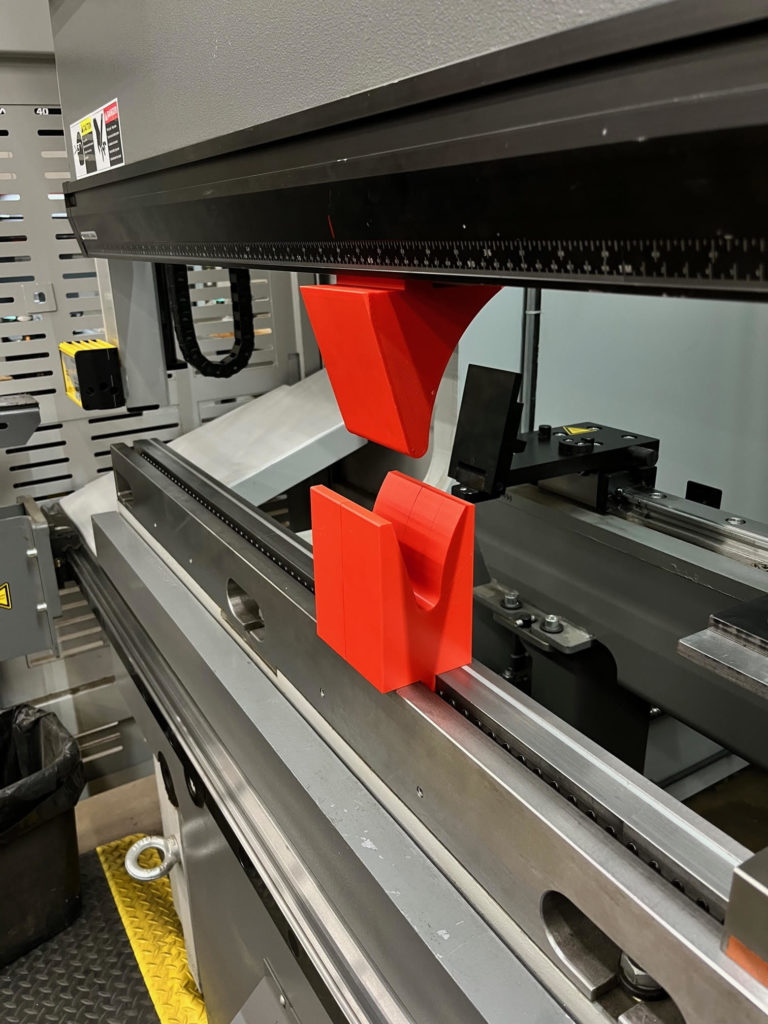




Benefits of 3D Printed Tools
The implementation of 3D printing technology into sheet metal forming has brought about a major transformation. Custom tools with intricate designs and exact measurements can be created in very short amounts of time due to this advancement, enabling the production process to become more cost-effective, faster and flexible when compared traditional metal tooling techniques. Among other uses such as for making bent brackets or embossed parts are louvers and grilles. These detailed components require little material waste while producing high quality results that could not have been achieved before now.
By greatly reducing lead times while decreasing costs associated with tooling investment, manufacturers benefit from much swifter iterations allowing them rapid modification capabilities regarding their design plans which was previously impossible without employing modern methods like 3D printed tools used within sheet metal forming processes today!
CNC Machines and Automation
Sheet metal forming has been revolutionized by the integration of CNC machines and automation technologies. This technology is ideal for sheet metal fabrication, as it enables precise control over processes related to shaping and cutting while being able to rapidly produce complex components in large quantities with a high degree of precision. Automation provides numerous advantages such as improved productivity, decreased lead times, higher safety standards along with cost-effectiveness. All key factors in increasing efficiency whilst ensuring the highest quality possible within this industry sector. The use of computer numerical controlled (CNC) machining combined with automation solutions makes production fast yet accurate even when dealing with low volume or diverse products which require tailor-made treatment specifically suited for each process component involved during manufacturing activities associated with sheet metal forming procedures.
Atlas Manufacturing: Expertise in Sheet Metal Forming
Atlas Manufacturing has been a dependable leader in contract manufacturing and precision sheet metal fabrication for more than 50 years. With an uncompromising dedication to delivering premium-grade items, they have managed to set the highest standards of quality throughout their industry sector. Their expertise with metals extends across various industries and applications, making them invaluable partners when it comes to sheet metal needs.
Industries Served
Atlas Manufacturing has a wide range of experience in metal forming, providing tailored services to many industries. From custom computer server cabinets for telecoms applications to sheet metal parts used in medical devices, the company is adept at understanding and delivering optimal outcomes based on each sector’s individual requirements. Their dedication to quality results in innovative solutions that give businesses confidence when they choose Atlas as their partner for sheet metal formation needs. A commitment to excellence makes them stand out from other providers within this market space.
Comprehensive Services
Atlas Manufacturing has comprehensive services to assist customers with their sheet metal forming projects. These include fabrication, powder coating, engineering and design, assembly as well as logistic support services that make sure top-notch quality is delivered all the time. With a facility covering 75 thousand square feet of space, it can handle jobs ranging from smaller prototypes up to massive production runs. This fact coupled with its commitment to great client satisfaction means Atlas Manufacturing retains an untarnished reputation in contract manufacturing circles for having dependable partnerships being established throughout this domain.
Atlas Manufacturing’s commitment to metal forming is exemplified in this custom 3D printed tool, which showcases their proficiency for creating innovative solutions. These images demonstrate the accuracy of design and high degree of precision required in sheet metal fabrication with such advanced techniques.
Advanced technology allows Atlas Manufacturing to push beyond conventional limits when it comes to producing top quality outcomes from material like sheet metal. All accomplished by using cutting-edge tools and processes that maximize performance while ensuring durability.
Best Practices for Sheet Metal Forming
Sheet metal fabricators must adhere to best practices for optimal forming outcomes. This involves taking design factors like material, thickness and bend radius into consideration when selecting the appropriate tools, as well as providing comprehensive operator training for maintenance purposes. Following these guidelines can assist in lowering waste, improving production efficiency whilst conforming with quality demands from different industries related to final products made of sheet metal components. By doing so they contribute not only to their own success but also enable growth within their business area connected with professional processes involving metal materials and formation techniques.
Emerging Trends in Sheet Metal Forming
The sheet metal forming industry is constantly evolving, and with it come the latest trends of robotic automation, additive manufacturing, along with advanced materials such as carbon fiber and composites. All these innovations bring about many advantages in terms of productivity, accuracy and versatility. Allowing manufacturers to make intricate components that have complex geometries.
In order for them to remain at the forefront within this rapidly changing field, they need strategies which ensure their success – such as being open-minded towards modern technologies & material science developments plus investing in employee training programmes or consulting other professionals who can provide additional knowledge on best practices when using metals & equipment, etc. Taking heed regarding customer needs/market trends alongside updating machinery are also equally important considerations so that fabrication processes generate quality parts from sheet materials accordingly.
Summary
The sheet metal forming process is a reliable and cost-effective way of creating custom components for an array of industries. By combining techniques such as bending, curling, ironing and utilizing tools like 3D printing and CNC machines to shape sheets made from various materials into intricate parts that meet exact specifications, the formation possibilities are endless!
Atlas Manufacturing leads in this field with their skillful services tailoring solutions to customer needs across many sectors. Continuously investing resources towards staying up on the latest trends so they can deliver superior quality work every time.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is forming in sheet metal?
Metal forming of sheet metal is the process of deforming this material into its desired shape, without cutting or removing any part. By using force to manipulate it plastically, a specific form can be achieved from the initial base material.
What is the best sheet metal for forming?
Steel is an ideal option for roll forming, thanks to its strength and durability. It can also be treated in a way that guards against corrosion.
What are the basic principles of sheet metal forming?
Sheet metal forming involves reshaping the material by exerting force on it without cutting or removing pieces, thus pushing the sheet beyond its yield strength and causing plastic deformation rather than failure.
What is sheet metal roll forming?
Roll forming is a procedure that employs numerous sets of paired rolls to reform metal sheet into the desired shape with successive alterations. This transforms it into an engineered profile, giving a unique form from what was originally only plain metal sheet.
What is precision sheet metal fabrication?
The process of precision sheet metal fabrication involves cutting, forming and bending thin sheets of metal into various components that possess exact specifications. It is an effective method for producing superior-grade parts with intricate shapes for different applications utilizing metallic materials.
