
What you’ll learn about sheet metal forming
By reading this article, you will learn:
– The definition, importance, advantages, and applications of sheet metal forming in precision fabrication.
– Fundamentals, materials, precision techniques, design principles, tooling, quality control, advancements, case studies, and future trends in sheet metal forming.
– The role of sheet metal forming in industries such as aerospace, automotive, electronics, and medical devices.
What is Sheet Metal Forming and Why is it Important?
Sheet metal forming, also known as precision sheet metal forming, is a crucial process in the manufacturing industry. It involves transforming flat metal sheets into desired shapes through mechanical and hydraulic processes such as bending, flanging, deep drawing, and stretching. This process is of utmost importance as it allows for the creation of complex geometries with high precision, making it indispensable in the manufacturing of intricate components.
Real-life examples of precision sheet metal forming can be found in the production of enclosures for electronic devices, complex brackets for aerospace applications, automotive body panels, and a wide array of consumer products. The ability to achieve tight tolerances and exceptional surface quality is essential in industries where precision and reliability are paramount.
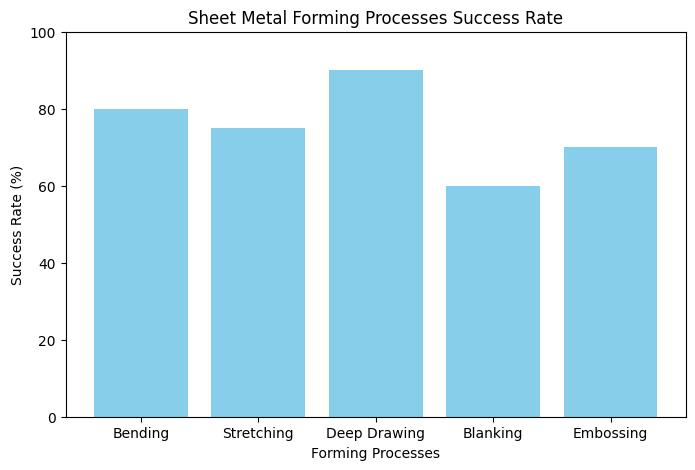
Fundamentals of Sheet Metal Forming Processes
Definition and Importance
Sheet metal forming involves the transformation of flat metal sheets into desired shapes through various mechanical and hydraulic processes. These processes include bending, flanging, deep drawing, stretching, and specialized techniques. The importance of sheet metal forming lies in its ability to create complex geometries with high precision, making it indispensable in the manufacturing of intricate components.
Role in Precision Sheet Metal Fabrication
In the realm of precision sheet metal fabrication, forming processes are instrumental in shaping raw materials into finished products with tight tolerances and exceptional surface quality. Whether it’s producing enclosures for electronic devices or intricate brackets for aerospace applications, precision sheet metal forming is the backbone of manufacturing operations.
Advantages and Applications
The advantages of sheet metal forming are multifaceted, including high production efficiency, material savings, and the ability to achieve complex geometries. Its applications span across diverse industries such as aerospace, automotive, electronics, and medical devices, where precision and reliability are paramount.
Relationship to Metalworking Industry
Sheet metal forming is intricately linked to the broader metalworking industry, as it often complements processes like cutting, welding, and assembly. Its seamless integration with other manufacturing disciplines underscores its significance in the creation of a wide array of products.

Materials and Alloys Utilized in Sheet Metal Forming
Aluminum Alloys
Aluminum alloys are extensively utilized in sheet metal forming due to their lightweight nature, corrosion resistance, and favorable mechanical properties. These alloys find applications in aircraft components, automotive body panels, and consumer electronics, where their high formability and strength-to-weight ratio are advantageous.
Stainless Steel Grades
The diverse range of stainless steel grades caters to various forming requirements, offering exceptional corrosion resistance, aesthetic appeal, and structural integrity. From kitchen appliances to architectural elements, stainless steel’s formability and durability make it a preferred choice in sheet metal forming.
Copper and its Alloys
Copper and its alloys, renowned for their excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, are utilized in sheet metal forming for applications in electrical components, heat exchangers, and architectural elements. Their malleability and ductility make them ideal for intricate forming processes.
Criteria for Selecting Suitable Alloys
When selecting materials for sheet metal forming, considerations such as formability, strength, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness play a pivotal role in determining the most suitable alloys for specific applications.
Material Suitability for Various Forming Processes
Different forming processes require materials with specific characteristics, and the suitability of alloys for bending, deep drawing, stretching, and other techniques is a crucial factor in achieving desired outcomes.
Influence of Material Properties on Forming
The properties of materials, including their yield strength, elongation, and work hardening behavior, profoundly impact the formability and manufacturability of sheet metal components. Understanding these properties is essential for successful forming operations.
| Precision Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| CNC Punching | Utilizes Computer Numerical Control for precise creation of perforations and forms in sheet metal. |
| Laser Cutting | Employs laser technology for accurate shaping and profiling of materials with exceptional precision. |
| Press Brake Forming | Uses mechanical or hydraulic presses for bending and forming sheet metal into desired geometries. |
| Hydroforming | Shapes sheet metal using high-pressure fluid, allowing for the creation of complex and seamless components. |
| Advanced Forming Technologies | Includes incremental forming, electromagnetic forming, and rubber pad forming for innovative shaping of sheet metal. |
| Integration of CAD/CAM | Optimizes design and production processes by integrating Computer-Aided Design and Manufacturing software. |

Precision Techniques in Sheet Metal Forming
CNC Punching
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) punching enables the precise and rapid creation of perforations, forms, and other features in sheet metal. This automated process is widely employed in the production of panels, enclosures, and brackets with intricate patterns and cutouts.
Laser Cutting
Laser cutting technology, with its exceptional precision and versatility, plays a vital role in sheet metal forming by enabling the accurate shaping and profiling of materials. Its non-contact nature and ability to cut various thicknesses make it indispensable in the fabrication of intricate components.
Press Brake Forming
Press brake forming, utilizing mechanical or hydraulic presses, is a fundamental technique for bending and forming sheet metal into desired geometries. Its ability to achieve precise angles and dimensions is crucial in the production of brackets, frames, and enclosures.
Hydroforming
Hydroforming involves shaping sheet metal using high-pressure fluid, allowing for the creation of complex and seamless components with minimal material waste. This technique is widely employed in automotive, aerospace, and plumbing industries for producing structurally efficient and lightweight parts.
Advanced Forming Technologies
Advanced forming technologies, including incremental forming, electromagnetic forming, and rubber pad forming, offer innovative approaches to shaping sheet metal, catering to specific requirements in different industries. These techniques push the boundaries of traditional forming processes, enabling the production of complex geometries with enhanced efficiency.
Integration of CAD/CAM in Forming
The integration of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software optimizes the design and production processes, allowing for the seamless translation of digital models into precise sheet metal components. This integration enhances accuracy and efficiency in forming operations.
Including real-life examples, case studies, and insights from industry professionals would enhance the article by providing practical application and depth of expertise in precision sheet metal forming.
Common Questions
What is precision sheet metal forming?
Precision sheet metal forming is the process of shaping and manipulating sheet metal to create precise and complex parts and components.
How is precision sheet metal forming different from traditional metal fabrication?
Precision sheet metal forming focuses on achieving tight tolerances and intricate designs, while traditional metal fabrication may involve less detailed shaping.
Who can benefit from precision sheet metal forming services?
Industries such as aerospace, automotive, electronics, and medical devices can benefit from precision sheet metal forming for their intricate part requirements.
What are the advantages of precision sheet metal forming?
Precision sheet metal forming allows for high accuracy, repeatability, and the ability to produce complex geometries with minimal material waste.
How can precision sheet metal forming help reduce production costs?
By minimizing material waste and allowing for efficient production processes, precision sheet metal forming can help lower overall production costs.
What if my design has very tight tolerances, can precision sheet metal forming still be used?
Yes, precision sheet metal forming is capable of achieving very tight tolerances, making it suitable for intricate and precise designs.
